Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy
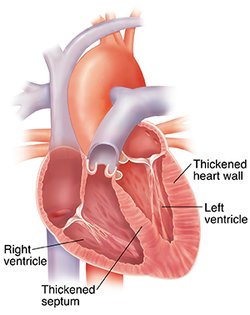
Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy is a condition in which the heart muscle grows abnormally thick and stiff. It most commonly affects the walls of the left ventricle and septum. This makes it hard for the heart to pump blood properly. Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy is usually inherited, although it often doesn’t show up until later in life.
Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy may raise your risk for heart failure. Over time, the heart muscle may become too stiff to let the ventricle fill completely. Then the heart can’t pump enough blood to meet the body’s need. This can cause symptoms such as breathlessness, chest pain, palpitations, tiredness, or exhaustion when trying to exercise. Let your healthcare provider know if you have these symptoms.
In some people, hypertrophic cardiomyopathy carries a risk for sudden cardiac death. If you have any passing out spells, tell your healthcare provider right away. If anyone in your family has died suddenly, especially at an unexpected age, tell your healthcare provider.
The condition can be managed, but there is no cure. Talk to your healthcare provider about treatment.
What are the symptoms of hypertrophic cardiomyopathy?
You may have no symptoms with hypertrophic cardiomyopathy. If symptoms do occur, they most likely appear when you exert yourself. Symptoms may include:
- Problems catching your breath
- Unexplained tiredness
- Lightheadedness, dizzy spells, or fainting
- Rapid, pounding heartbeat
- Chest tightness or pressure
- Swollen feet or ankles
- Unexplained weight gain
What happens in your heart?
As the walls of the heart muscle thicken, it becomes harder for the heart to move blood efficiently through the chambers. Thick walls may block blood from flowing freely out to the rest of the body. It may also damage heart valves causing blood to leak backwards. A stiff heart muscle can’t relax between pumps the way it should. This prevents adequate filling of the chambers and results in lower blood flow to the body with each pump. In some cases, the heart may develop an arrhythmia and beat irregularly (too fast and out of rhythm).
Treatment
There is no cure for hypertrophic cardiomyopathy, but treatment can help keep your condition from getting worse. And it can reduce your symptoms. Treatment may include medicines to help your heart pump more effectively, or to reduce arrhythmias. In some cases, surgery can destroy or remove thickened tissue to improve blood flow. Your healthcare provider will work with you to develop a treatment plan to help you feel better now and prevent problems in the future. It’s very important to follow the treatment plan exactly as directed. If you have questions or problems, talk to your healthcare provider.